
Verified Mark Certificates
A Verified Mark Certificate (VMC) is a digital certificate issued by certificate authority that verifies the ownership of a logo. Before getting a VMC, the logo must be a registered trademark.
Before the message is viewed, VMCs allow companies to display a trademarked brand logo next to the “sender” field in customer inboxes, acting as validation of the company domain’s DMARC status and authorised identity. It’s the email counterpart of a social networking checkmark, with additional validation and security criteria to help safeguard customers and brands from phishing and spoofing attempts.
How Do VMCs Work?
Logo-verified email is part of a groundbreaking initiative—in cooperation with Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI) and email client providers— to promote a consistent, trusted and visually authenticatable email experience for both businesses and consumers.
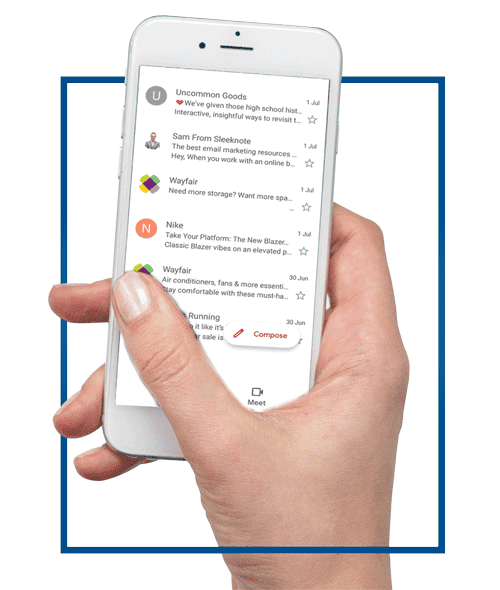
Here how it works:
Verified Mark Certificates are now available for purchase from WebNIC. A VMC is the only way you can display your logo on verified emails.
Before you can display your logo, email clients must be able to validate that you are enforcing Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) standards, which help to reduce phishing and spoofing attacks by giving your organization more control over your emails.
Once you’ve demonstrated DMARC enforcement, you will be able to upload your trademarked and validated logo for display within email clients. If you have multiple logos, you can choose which will render for each communication flow.
VERIFIED EMAIL BENEFITS THE WHOLE ORGANIZATION
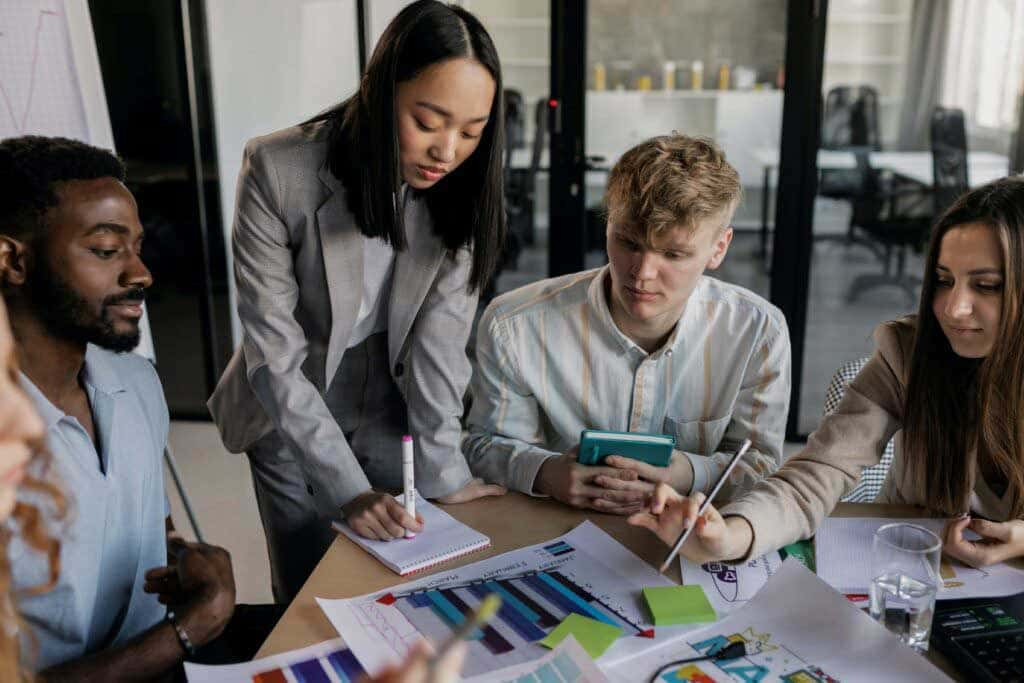

VMC BENEFITS FOR MARKETERS
- Instead of default initials, customers see your logo—before they even open your email.
- Deliver a more authentic, recognizable and unified experience.
- Instantly associate trust with your email communications. And your logo.
- Stand out from the crowd and let customers know you’ve made their security a priority.
- Increase visibility, recall and engagement—including a 10% increase to engagement rates.
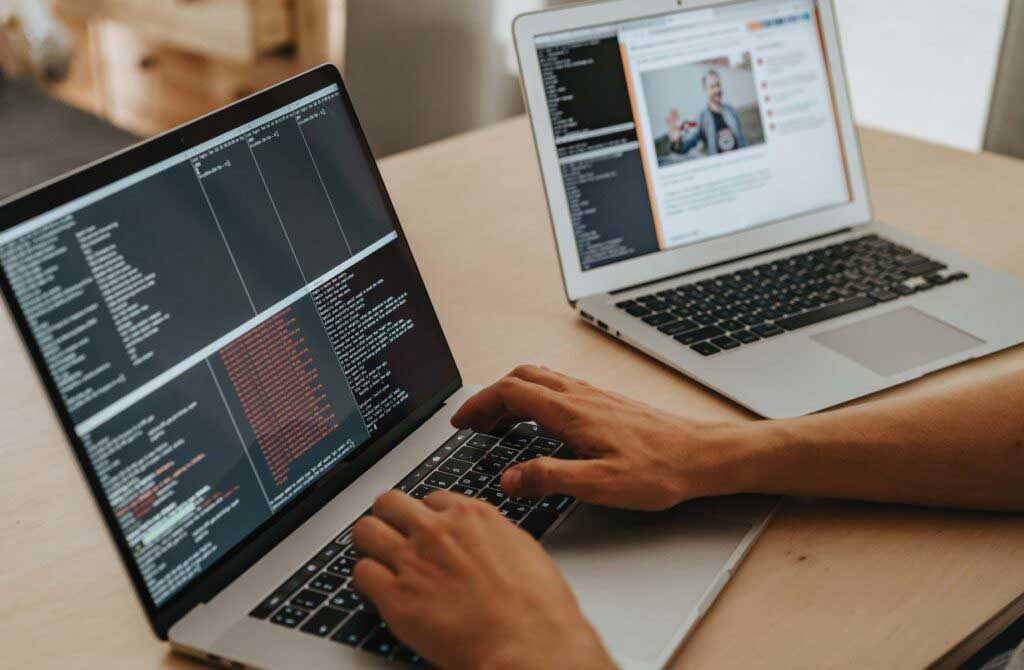

DMARC BENEFITS FOR IT
- Demonstrate the highest level of email security practice through DMARC compliance.
- Make it harder for bad actors to target your customers with identity-focused attacks like spoofing and phishing.
- Get better visibility and control over the messages sent and received by your domain.
- Gain clear insight into the types and frequency of attacks targeting your domain.
- Ensure legitimate emails are delivered reliably, without anything slipping through the cracks.
Protect Your Brand Reputation And
Increase deliverability

Upgrade the inbox experience

Increase open rates

Improve email security
Frequent Asked Questions
A Verified Mark Certificate, abbreviated VMC, is a special kind of digital certificate that allows companies and individuals to display a trademarked logo in the list view of recipients email inboxes next to the sender field.
A VMC is the last step in a chain of security and identity measures related to DMARC adoption. To acquire a VMC, the purchaser must demonstrate that their logo is legally trademarked with an approved trademarking body, authenticate the physical identity of the purchaser through an in-person validation meeting, and confirm ownership of the email domain to which the VMC is issued.
VMCs are only displayed for senders that are maintaining enforcement of DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) policies and that have a BIMI record in their DNS. Companies are adopting DMARC with enforcement as a means of combatting unauthorized use of email domains, in order to protect both organization and recipients of that organization’s emails from identity-targeted attacks like spoofing and phishing.
The VMC enables the displayed logo to function as a visual identifier of an organization’s secure, validated identity and that the organization has adopted DMARC with enforcement.
In order to get a VMC, organizations must go through a series of validation procedures similar to getting an EV SSL certificate. During the process, an individual’s identity validation is required as well as face-to-face confirmation by a notary, lawyer or solicitor. DigiCert’s validation team will also have a video call with the applicant where they hold their ID in front of the camera. Finally, DigiCert must also validate that your logo is officially and legally trademarked and formatted correctly.
Before you can qualify for a Verified Mark Certificate, your organization needs to meet several key requirements to validate your domain and brand identity.
1. Implement DMARC standards for your organization. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is an email authentication, policy and reporting protocol that makes it harder for bad actors to spoof your brand, and gives you more visibility and control over emails sent and received by your domain.
2. Trademark your logo. To qualify for a VMC, your logo must legally trademarked with the appropriate office for your geographic region.
3. Convert your logo file to the .SVG format.
4. Purchase a VMC and complete validation.
5. Install your VMC. After you have submitted your SVG logo file to DigiCert, you will receive a file containing a PEM-encoded certificate chain. Both the SVG and the certificate chain file must be placed on a publicly accessible server and be accessible via https (HTTP will cause a failure). You will then need to update your BIMI record with the correct URL and file location
Yes, a registered trademark is one of the requirements in order for a VMC to be issued.
No, only the registered logo that will be used for BIMI needs to be registered.
Currently, the VMC Guidelines officially recognize below intellectual property offices:
- United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO)
- Canadian Intellectual Property Office
- European Union Intellectual Property Office
- UK Intellectual Property Office
- Deutsches Patent- und Markenamt
- Japan Trademark Office
- Spanish Patent and Trademark Office O.A.
- IP Australia
- Intellectual Property India
- Korean Intellectual Property Office
- Instituto Nacional da Propriedade Industrial
To qualify for a VMC, your organization has to trademark their logo with one of the intellectual property offices above, if that hasn’t been done already.
When certificate authority validates your logo for inclusion in a VMC they must find it registered with one of the intellectual property offices listed above. We are not familiar with the laws of each country and how to register your logo as a trademark beyond what we’ve shared above. That said, if your logo is registered as an active trademark in one of the current recognized intellectual property offices, then we will use that source for confirming validation.
VMCs increase trust in emails because they certify that a brand and its logo are authentic by way of Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI) and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC). VMCs allow a brand’s logo to be viewed inside email clients once the brand has passed DMARC authentication checks to ensure the organization is not being impersonated.
According to DMARC.org:
“DMARC stands for “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance”, is an email authentication policy and reporting protocol. It builds on the widely deployed SPF and DKIM protocols, adding linkage to the author (“From:”) domain name, published policies for recipient handling of authentication failures, and reporting from receivers to senders, to improve and monitor protection of the domain from fraudulent email.”
In simplified terms, DMARC gives security professionals more transparency and better control over the emails sent and received by their domain in order to identify and block or quarantine potentially fraudulent emails more quickly. It’s a standard that helps to protect both consumers and brands from phishing and spoofing attacks.
DMARC enforcement, sometimes referred to as DMARC compliance or DMARC deployment, is a means of enabling Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, or DMARC, within an organization.
DMARC is a TXT record stored in DNS that gives email receivers the ability to check the authenticity of received mail. It is designed to fit into an organization’s existing inbound authentication process and helps email receivers determine if a message “aligns” with what the receiver knows about the sender. Organizations have three policy options to handle “non-aligned” messages: “p = none” (no enforcement), “p = quarantine,” “p = reject.” For DMARC to work properly, Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeysIdentified Mail (DKIM) protocols must be set up beforehand.
Three quarters of organizations were targeted by phishing and spoofing attacks in 2020, and 96% of those attacks were delivered by email. 36% of all breaches were caused by phishing attacks alone (Verizon Report).
DMARC-enforcement is important because it gives organizations greater visibility into and control over the messages sent and received by their domain. This, in turn, allows organizations to identify and quarantine or reject potentially fraudulent email faster.
Growth in adoption of DMARC is extremely important. Very much like quarantining works to combat a physical pathogen, the more organizations who enforce DMARC, the fewer easy targets are available, and the safer email becomes for all users.
According to DMARC.org, “DMARC is designed to fit into an organization’s existing inbound email authentication process. The way it works is to help email receivers determine if the purported message “aligns” with what the receiver knows about the sender. If not, DMARC includes guidance on how to handle the “non-aligned” messages.”
Essentially, DMARC goes a step further than the widely adopted SPF and DKIM policies to create simple, scalable and effective methods of confirming an email’s authenticity, reporting questionable and fraudulent messages, and preventing delivery of phishing attacks. By reliably cutting off malicious messages before they are delivered, DMARC denies attackers their primary vector and dramatically reduces an organization’s vulnerable surface.
BIMI, Brand Indicators for Message Identification, is an emerging standard for inserting registered trademarks inside email clients that makes it simple for organizations to display their brand on emails. This means that when a user opens up an email on an email client that supports it, organizations that have adopted BIMI will be able to present their registered logos to end-users in a secure, interoperable way.
Companies enable DMARC Email service providers validate the sending domain Only verified emails reach the inbox The validated Verified Mark Certificate logo displays to make this train of trust visible and apparent. This widespread deployment is particularly important, because as the number of organizations enforcing DMARC increases, the targets for phishing and spoofing attacks are reduced and email as a whole becomes safer and more trustworthy.
Yes, BIMI will show the registered logo on any email from a BIMI-enabled domain, as long as a VMC has been issued and it is DMARC compliant.
BIMI is the protocol that enables organizations to display a registered logo alongside email messages. A VMC verifies that the logo belongs to that company and that it is a legitimate company. A VMC ties into the BIMI record as a tamper-proof security measure.
Verified Mark Certificates are the last step in a series of identity authentication and security validation checks. Your organization’s DMARC enforcement is validated by the email client via confirmation of your BIMI record and VMC-enabled logo. If everything checks out, your logo is displayed, serving as a visual indicator of your message’s authenticity, which in turn increases engagement and builds brand recognition.
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, or S/MIME, is an internet standard to digitally sign and encrypt email messages. It ensures the integrity of email messages remains intact while being received. By using digital signatures, S/MIME provides for authentication, message integrity, and non-repudiation of origin. In addition, S/MIME includes encryption that strengthens privacy and data security for electronic messaging.
Emails messages can be secured and encrypted with S/MIME, or Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions and PKI, or digital certificates. S/MIME combined with digital certificates can provide data encryption, message integrity and non-repudiation of message origin. The DigiCert® PKI Platform for S/MIME includes S/MIME key escrow service, certificate lifecycle management and the trusted DigiCert Certificate Authority (CA).
Email users can prevent email phishing by enforcing a DMARC policy that effectively screens out emails that are fraudulent or a phishing attempt. DMARC goes a step beyond SPF and DKIM policies to ensure sent emails are authentic.
In addition, Verified Mark Certificates with DMARC enforcement help to ensure an organization isn’t being impersonated and that a brand is represented by its authentic logo in an inbox.

