In today’s fast-paced digital world, security is more important than ever. With so much sensitive information being shared online, it’s crucial to ensure that personal data is secure and encrypted. One way to do this is by using digital certificates, which serve as a form of identification and authorization for online interaction. However, managing these certificates is not a simple task, especially for organizations with numerous certificates to handle. That’s where a solution called Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) comes in.
About Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM)
Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) is the process of managing digital certificates, from the time of their creation to expiration, including the renewal and revocation of certificates. A CLM console is designed to help organizations to manage their digital certificates, making sure that their digital certificates are always up-to-date, secure, and in compliance with industry standards and regulations. DigiCert, Entrust, GlobalSign, and other providers are just a few that provide CLM solutions.
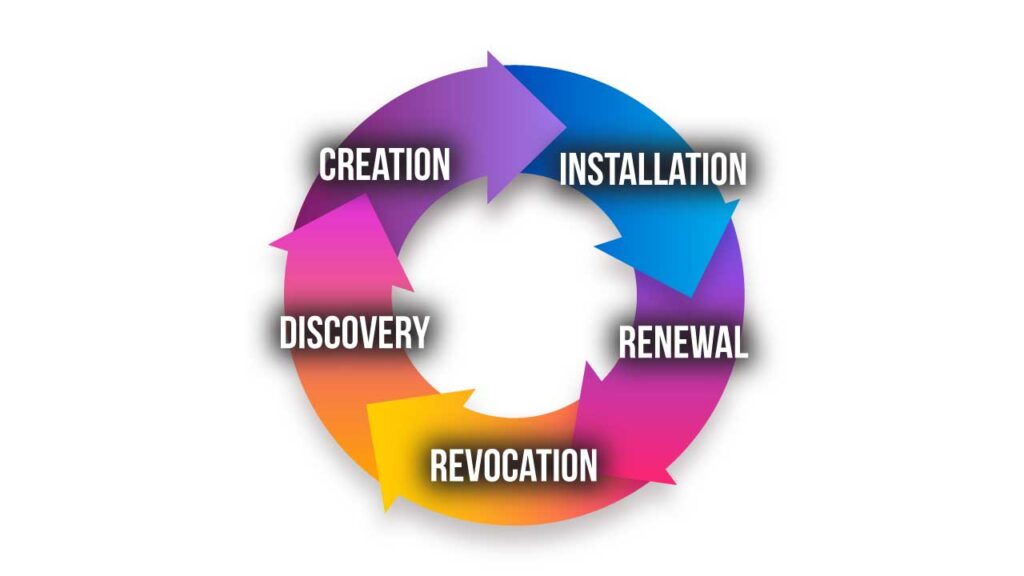
The Stages of Certificate Lifecycle Management
There are several different stages in the digital certificate’s lifecycle, and it is not set in stone. In this section we will delve into five stages of the digital certificate lifecycle: discovery, creation, installation, renewal, and revocation. Let’s take a closer look at each of these stages.
- Discovery
The discovery stage is where organizations track and monitor all the digital certificates within their network. This involves identifying missing, expired, or compromised digital certificates and categorizing them. Organizations typically use automated tools to scan their networks and identify any certificates that are currently in use. This stage is critical because it allows organizations to identify any expiring certificate, potential risks or vulnerabilities that may exist. - Creation
This stage involves generating a public-private key pair, creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), and submitting the CSR to a Certificate Authority (CA) for verification. The CA will verify the requester’s identity and issue the digital certificate to the requester. - Installation
Once the digital certificate is issued by the CA, it has to be set up on the server or device it is intended for. This is to ensure that any communication between the server or device and other parties is encrypted and secure. - Renewal
Certificates currently have a lifetime of approximately 398 days, or 13 months, after which they expire and can no longer be used. To ensure seamless website security, it’s important to renew digital certificates before they reach their expiration date. Just like the creation stage, the renewal of a certificate requires generating a new CSR and submitting it to the CA for verification. - Revocation
In some cases, it becomes necessary to revoke a digital certificate prior to its expiration date. This could be due to a security breach, a lost or stolen private key, or a change in the certificate holder’s status. When a certificate is revoked, it is added to a Certificate Revocation List (CRL), which informs users that the certificate is no longer valid and should not be trusted.
Managing the lifecycle of digital certificates is complex and requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices. However, the benefits of certificate lifecycle management are numerous:
- CLM ensures that digital certificates are always up-to-date and secure, reducing the risk of security breaches and other threats;
- It also helps organizations comply with industry standards and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR);
- By automating the certificate lifecycle management process, organizations can save time and reduce the cost of manual certificate management.

Case Study
AVEVA, a company that drives digital transformation through industrial software, was facing a challenge in managing digital certificates across its 80 locations in more than 40 countries. Their approach was piecemeal – their software developers and IT staff bought certificates as needed for their projects or users, respectively, from multiple certificate authorities (CAs) without a centralized system or standardized process. As a result, they faced gaps in TLS management, higher costs, and difficulty in tracking expiring certificates. However, AVEVA found a solution in CertCentral – a certificate management platform by DigiCert. DigiCert CertCentral enabled them to centralize TLS operations, streamline processes, and integrate code signing, which was a game-changer for AVEVA’s developers. The platform’s Discovery tool made it easier for IT staff to track where legacy certificates were acquired, which was crucial for a multi-company merger environment. CertCentral helped AVEVA increase efficiency and optimize client resources through better monitoring and control. Overall, the solution was a perfect fit for AVEVA’s needs, and it provided a holistic view of how the company approached front-end server security.
DigiCert CertCentral and WebNIC
As a Platinum Partner of DigiCert, WebNIC is proud to offer the DigiCert CertCentral solution for enterprises. CertCentral is a comprehensive certificate management platform that simplifies the process of managing SSL/TLS certificates. With CertCentral’s certificate lifecycle feature, you can easily track every certificate, help you avoid the hassle and improve security. If you’re looking for a reliable, easy-to-use certificate management solution, DigiCert CertCentral is an excellent choice. Contact us today at [email protected] to learn more about how WebNIC can help you implement CertCentral in your organization.

Author: Chan Kang

Designer: Jackson














































![How to remove Media Player Update pop-ups [Chrome, Firefox, IE, Edge]](https://www.myantispyware.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Media-Player-Update.jpg)