What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is an important part of a website URL. It acts like an address to a website on the Internet, just like an address to your physical house in the real world. In order to understand what is a domain name and the reason behind using it, we must first understand the concept of IP address.
The Internet is a giant network of computers connected with each other. The way to identify each device is through assigning a unique IP address to each of them. An IP address is a string of numbers separated by full stops, such as “104.20.73.209”. It acts as the address of a device on the Internet.
A website is hosted on a server (also a device connected to the Internet). Therefore, the server will have its own unique IP address. When a user uses a browser to visit a website, he/she needs to enter the IP address of the server hosting the website, so that it can establish a connection with it to load the website. However, this is not how it works as it is difficult for humans to remember a string of numbers. Furthermore, with more than 100 million of servers hosting billions of websites on the Internet, it is impossible for a human to remember millions of IP addresses.
For this reason, the domain name was introduced in order to solve this problem. It simplifies the process for users to visit their intended websites. Instead of remembering a string of numbers, it is easier to remember texts. It acts like a pointer to a specific IP address on the Internet. The below illustration shows the different parts of a website URL and where the domain name is.
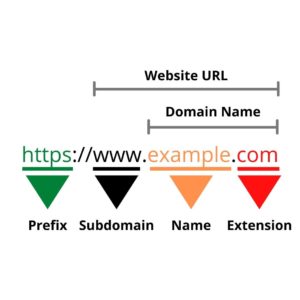
How Does a Domain Name Work?
When users enter the domain name in a browser, the browser connects to the Domain Name System (DNS), a global network of domain name servers located worldwide. The DNS is like a distributed database which stores domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. The requested domain name is then matched against the data in the DNS, and translated into an IP address. The browser then establishes a connection with the resulting IP address, which will then forward the initial browser request to the server hosting the intended website. The website server will then respond to the browser request and returns data to the browser to load the website for the users. An illustration below shows the entire process of how a domain name works.
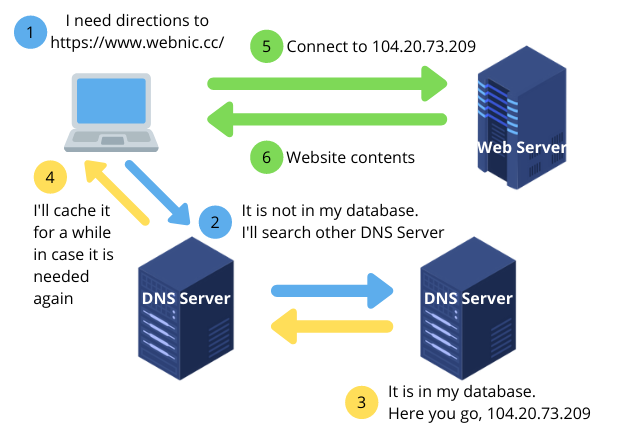
Types of Domain
Aside from the common .COM websites you see on the Internet, there are actually many other types of domain names on the Internet. The type of domain name depends on the extension used by the domain name. There are two main categories of domain names, namely the generic Top-level Domain (gTLD) and the country code Top-level Domain (ccTLD). Below is a description of each category of domain name and some examples for your understanding.
Generic Top-level Domain (gTLD)
gTLD is as the name implies, a generic domain name. It can be registered by anyone from anywhere. The most commonly known gTLD is .COM, .NET, .ORG, .BIZ, and .INFO. There are also some other restricted gTLDs, reserved for specific uses, such as .GOV for government, .EDU for education institutes or .MIL for military. gTLD is not restricted to any geographical location or country. Anyone can register a gTLD, regardless of where they are. Examples include “facebook.com”, “wikipedia.org”, “slideshare.net” etc.
In recent years, the gTLD has expanded to include many newer gTLDs introduced by ICANN since 2013. Some examples of these new gTLDs include .BLOG, .ONLINE, .SHOP, .TECH, .XYZ and many more.
Country Code Top-level Domain (ccTLD)
ccTLD is a type of domain name that is restricted to a certain country or location. It uses the country codes standard as the extension like .MY, .SG, .UK etc. Therefore, ICANN assigns every country its own extension, and each country is given the authority to operate their own extension. Some countries open their ccTLD registration to the public, while most countries establish terms and conditions to register for their extension. As a result, ccTLD is the opposite of gTLD and registering it is subject to certain terms and conditions, and the process is more time-consuming. Usually, the conditions to register a ccTLD is that the registrant must be a citizen of the specific country or the business needs to be registered with the local governing body. Examples of ccTLD include “webnic.cc”, “redd.it”, “instagr.am”, “youtu.be” etc.
If you are interested, check out this list of the most popular ccTLDs by the number of domains registered here.
If you are still unsure about the difference between these two TLDs, click the link here to read more!
A Domain Name is not a Website or a Hosting
Another thing that many people are confused with is the difference between a domain name, a website and a hosting. Many people seem to think that they mean the same thing, but they are actually not.
A website is made up of many files which contain information and contents. These files work together to ensure that the website can be viewed when opened on a browser. They are crucial for a website to work, just like the components of a machine.
Next, we need a place to store these files. The place where the files are stored is called a server. Whenever a request comes in for the website, the server will respond to the request and load the files. For this, we call it a hosting service. You are essentially buying a hosting service to store your website’s files on a server, so that they can be loaded when there is a request for your website. This is hosting.
Lastly, the server that hosts our website files will have an IP address on the Internet. As mentioned in the section explaining how domain names work, we need a domain name to direct users to know how to find our website on the Internet.
Domain name, website and hosting are not the same, but all three of them are necessary for a website to work properly. They work together to deliver a website browsing experience to users. Note that you can buy domain name and hosting separately as two different services, but then you will need to do a bit of configuration to connect them.
How Does Domain Registration Work?
The domain registration process is facilitated through a few major parties, namely ICANN, a domain registry, a domain registrar and a domain reseller.
ICANN is the organisation solely in charge of maintaining and regulating the domain industry. It maintains and coordinates each top-level domain (TLD), while also taking care of security and stability of the domain root network and its infrastructure. ICANN appoints which party is in charge of managing the domain names records registered under each Top-level Domain (TLD).
The party appointed by ICANN is what we call a domain registry. It is in charge of managing all the domain names record in a database. According to the definition of a domain registry by ICANN, a domain registry is the party responsible for accepting domain name registration requests from registrars, maintaining a database of the necessary registration data associated with domain names, and providing name servers to publish the zone file data (e.g., the list of all the domain names and their associated IP addresses) throughout the Internet.
Next, a domain registrar is a qualified party, accredited by ICANN to perform domain names transactions, namely registration, renewal and transfer. To perform these processes, a domain registrar needs to meet strict requirements established and usually has an agreement with a domain registry. It usually needs to build and maintain infrastructure to connect with a domain registry to perform domain names transactions.
Finally, domain resellers are parties who deal with end users who are interested to buy a domain name. They are affiliated or under contract with registrars to promote the registrars’ products and services to end users. They are like the sales representatives of a domain registrar. We at WebNIC are currently looking to partner with more domain resellers. If you are interested to become a reseller, contact us at inquiry@webnic.cc. We offer a comprehensive web service solution reseller experience.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you to gain a better understanding on what is a domain name and how it works. If you are interested to join the domain industry and you are looking for a domain registrar to partner with, WebNIC is the perfect choice. We are a trusted domain registrar with more than 20 years of experience in the domain wholesale and reseller service. We offer a wide range of domains to help you to become a domain reseller and grow your domain business with us. We also offer SSL certificate wholesale service, complete web security solution and digital brand management service.
About WebNIC
WebNIC is an accredited registrar for ICANN, and various countries including Asia, Europe, America, Australasia, and Africa. With offices in Singapore, Malaysia, Korea, Indonesia and Taiwan, we serve 4,500+ active resellers over 70 countries. To join us and become a reseller, live chat with us or email us at inquiry@webnic.cc.

